- Phan, M H, Harris LR, Kingdom F. A perceptual bias in the perception of falling objects. Perception 53 (3) 197-207
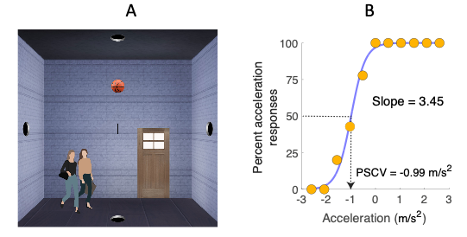
- J÷rges B, Harris LR (2024) The impact of visually simulated self-motion on predicting object motion. PLOS ONE (in press)
-
J÷rges, Bj÷rn, Nils Bury, Meaghan McManus, Ambika Bansal, Robert S. Allison, Michael Jenkin, and Laurence R. Harris. ôThe Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Microgravity and Body Orientation Relative to Gravity on Perceived Traveled Distance.ö Npj Microgravity 10, no. 1 (March 13, 2024): 28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41526-024-00376-6.