 |
Exercise
Recent Purchase |
Think of a
recent purchase you made and try to remember the steps you
went through in getting to the decision to buy (bring it to
class if you can). We will draw on these experiences in
class as we go through the steps of the consumer's decision
making process.
|
|
Consumers
as Problem Solvers
|
Perspectives on
Decision Making
| Rational |
 |
|
Behavioural Influence |
 |
|
Experiential |
 |
Types of Consumer
Decisions
|
Problem Recognition
The Marketer's Role:
Primary and Secondary Demand
Information
Search
|
Type
of Search
| Internal

|
External

|
| |
|
Deliberate
 |
Accidental
|
|
|
The
Economics of Information
Rational Searches
Bias
|
|
How
Much Search?
Information Available
Prior Expertise
Risk
|
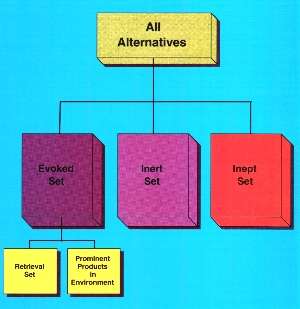
Evaluation of Alternatives
|
Identifying Alternatives
|
|
Product Categorization
|
|
Product Choice: Choosing Among Alternatives
|
|
Cybermediaries
|
Heuristics 

|
Brand Loyalty vs Habit
Inertia
|
Decision Rules
|
Non-Compensatory
(true story)

"an MG or nothing"
|
Compensatory
Simple Additive:
a car with as many good qualities as possible
Weighted
Additive: A car, in my favourite colour

|
|
Chapter 11 Group Influence
and Social Media
 |
Exercise
Meaning of Possessions |
We will watch Russel
Belk's film "The Deep Meaning of Possessions"
made in 1987, which started a revolution in how we view
the study of the field of Consumer Behaviour, and use it
to review the concepts of group influence.
|
|
Reference
Groups
We are motivated by desire to please others
Science shows even rats & cockroaches
prefer familiar things
 |
Types of Reference Groups
Normative vs Comparative
Formal vs Informal
Membership vs Aspirational
Identificational and deindividuation
Positive vs Negative
|
The
Power of Reference Groups
Sadly, people will often do things
in groups that they'd never do alone, think about lynchings
Types
of Power
Referent
Information
Legitimate
Expert
Reward
Coercive
Conformity
 |
Types of Social Influence
Normative vs Informational
Brought on by
cultural pressures
fear of deviance
commitment
group unanimity
gender influences
susceptibility to interpersonal influence
|
Social Comparison
Compliance and Obedience
Tactical Requests - foot-in-door, low-ball, door-in-face
Group Effects - risky shift, diffusion of responsibility,
decision polarization, social loafing
Resistance to
Influence
anti-conformity vs independence
reactance and uniqueness
Word-Of-Mouth
Communication
|
Dominance
Word of Mouth is a stronger determinant
of bank patronage than advertising
yet banks pour
millions of dollars into advertising
Why?
Factors Encouraging WOM
involvement
knowledge
concern for someone else
to reduce uncertainty
Negative WOM
Rumours
Boycotts
|
Opinion Leadership
|
Opinion Leaders
Market Maven
Surrogate Customer
Sociometric Methods
Diffusion of Innovation
|
(This outline does not follow
the new Chapter 11 on Social Media)
Time for Group Meetings
|