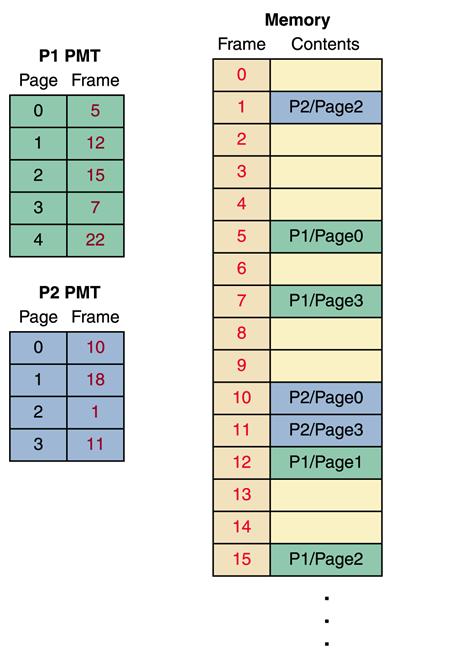
Paged memory technique (Dale and Lewis, Chapter 10.3, Process Management)
A memory management technique in
which processes are divided into fixed-size pages and stored in memory frames
when loaded into memory
Page-map table (PMT) A table used by the operating system to keep track of page/frame relationships
– Frame A fixed-size portion of main memory that holds a process page
– Page A fixed-size portion of a process that is stored into a memory frame
|
|
A logical address in a paged memory management system begins as a
single integer value relative to the starting point of the program, as it was
in a partitioned system. This address is modified into two (2) values by dividing the address by the page size:
e.g., Logical address of 2566, with a page size of 1024, corresponds to the 518th byte of page 2 of the process. 2566/1024
= 2.5058 Page =
2 Offset = 1024*0.5058 = 518 <page, offset> - <2,518>
|
e.g., If process 1 is active and Page Size = 1024
A logical
address of <1,222>
- Look up the frame # in PMT- Page 1 of process 1 is in frame 12
- Multiply the frame # by the frame size - Frame# * PageSize + Offset = 12 * 1024 + 222 = 12510
- The corresponding physical address is: 12510