Synapse
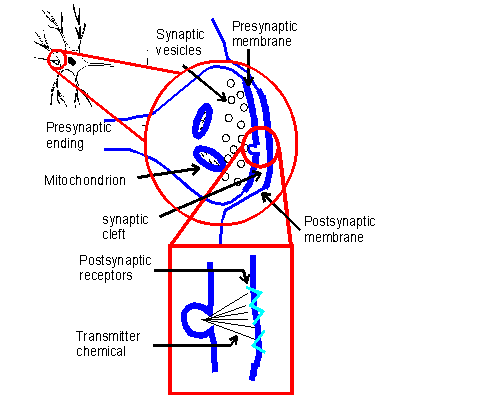 Impulses are
transmitted from neuron to neuron by the release of a transmitter
chemical across synaptic clefts which separate neurons.
This transmitter chemical is stored in synaptic vesicles of the presynaptic ending. One of the commonly referred to transmitter
chemicals is acetylcholine..
Impulses are
transmitted from neuron to neuron by the release of a transmitter
chemical across synaptic clefts which separate neurons.
This transmitter chemical is stored in synaptic vesicles of the presynaptic ending. One of the commonly referred to transmitter
chemicals is acetylcholine..
When an impulse arrives at a presynaptic ending, calcium ions cause the vesicles to
fuse with the presynaptic membrane and the transmitter chemical
in these fused vesicles is ejected into the synaptic cleft.
The transmitter chemical diffuses across the cleft and combines with the postsynaptic receptors. Depending on the postsynaptic
receptor, the transmitter chemical will produce either an excitatory postsynaptic
potential (EPSP) or an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP). An EPSP has the effect of depolarizing the neuron and the IPSP
has the effect of hyperpolarizing it.
What do you suppose happens if both an EPSP and an IPSP occur at a given neuron? The
concept of neural summation provides the answer.
Table of Contents
Subject Index
Table of Contents [When not using framtes]
 Impulses are
transmitted from neuron to neuron by the release of a transmitter
chemical across synaptic clefts which separate neurons.
This transmitter chemical is stored in synaptic vesicles of the presynaptic ending. One of the commonly referred to transmitter
chemicals is acetylcholine..
Impulses are
transmitted from neuron to neuron by the release of a transmitter
chemical across synaptic clefts which separate neurons.
This transmitter chemical is stored in synaptic vesicles of the presynaptic ending. One of the commonly referred to transmitter
chemicals is acetylcholine..