|
Chapter 8: Developing and Managing Products and
Services
I. What is a Product?
Goods, Services, Experiences, Organizations, Persons, Places, Ideas, and
combinations of any of these
(Your text uses "product" in many
places where I believe it should say "good", since "product"
contains both goods and services, but I use their terminology in
order not to confuse you as you work through this webpage along
with your text).
A product is anything
that might satisfy a want or need, whether it is a:
 Good Good |

Service |

Event |

Person |

Place |

Business or Organization |

Socially Responsible Act |

Experience |

Combination |
Here, from this course
a few years ago, is a
description of a product that is an experience, sent by Todd Brady |
| Todd writes: A word of
advice to everyone: I just returned from an establishment
called “Casino Niagara”. The product offering isn’t very strong. I
sat at a table and gave the nice man in a tuxedo money. He then
gave me a bunch of coloured tokens; he then told me to put them
down on the table. He then took those tokens back and told me to
go home because I didn’t have any more. I don’t know if this
product “gambling” is going to fly. This product may be good,
maybe just not this specific business. I plan to try out other
product offerings at competitors in a city in the Nevada desert. |
 |
 |
Exercise
Experience as Product |
Report on an "Experience" you have purchased. What "extra
value" did it offer you beyond just a product?
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
The Good/Service Continuum
 |
Exercise
- Plan
GS Continuum |
Explain
where on this continuum (from left to right) your
Marketing Plan product will fit
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
Levels of
Products and Services
 |
Exercise:
Plan
Levels of Product |
For
your Marketing Plan product, list the Actual Product,
the Core Benefit, and at least two parts of the
Augmented Product.
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
Product as the packaging of a solution
Charles Revson

"In the factory we
make cosmetics... |

...in the drugstore we
sell hope." |
Theodore Levitt
"A
purchasing agent buys 1/4 inch holes, not a 1/4 inch
drill." |
 |
Elmer Wheeler
"Sell the
Sizzle, not the steak." |
 |
 |
Exercise:
Plan
Packaging a Solution |
Describe
the problem for which your Marketing Plan product will
be a solution.
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
Product and Service Classifications
|
1. Consumer Products |
|
2.
Industrial
Products |
 |
|
Materials
and Parts
> Raw Materials
> Manufactured Materials
> Parts
|
Capital
Items
> Installation
> Accessory Equipment |
Supplies
and Services
> Operating Supplies
> Repair and Maintenance Items |
|
3. Organizations, Places, and
Ideas
Marketing techniques can be used
to sell things other than toothpaste. We regularly see ads for
the Red Cross, politicians running for office, Toronto as a
tourist destination now that SARS is over (we hope), and ideas
like quitting smoking.
One of the most important social uses of
marketing is what is called Social Marketing, where we use the
techniques and theories of marketing to sell an idea that will
be good for society. Click here to read about what Social
Marketing is and is not. We teach a 4000 Honours level
course on Social Marketing AK/ADMS4280
3.0.
Industrial
Products
The main classification difference between consumer products
and industrial ones is the purpose for which they are purchased.
If you buy something for your own use, it's a consumer product. If
someone buys somoething to resell or to use in building something
else, it is an industrial product.
II. New Product Development
New Product Development Strategy
The following story comes from a graduated York student
Danny Hadida, who took several marketing courses with me and who
now comes back to speak to marketing classes. A few years ago, he
introduced a new product to the market. The product failed miserably,
but he learned some solid marketing lessons, and he also used the video
and presentation he created about the experience to land himself a
teaching job in a Toronto High School, after completing his teaching
certification.
The Study
Buddy
Eight Dangers of New Product Introduction
- Danny Hadida |
 |
SIGNALS
Don't
ignore the danger signals hoping they'll go away.
During the creation and research of the Study Buddy I
received a lot of information that was contradictory to my ideas
and plans. I had
subscribed to a “never give up” attitude towards the Study
Buddy, so instead of changing direction I tried to “keep
positive”. For
example, when speaking to people who were not interested in
purchasing the product, I discarded their comments, thinking,
“well they are just not a part of my market”. The lesson I learned here was:
read the signals -- separate the product from the person; revise
goals and objectives following the uncovering of new relevant information. Entrepreneurs should not confuse changing their goals
with quitting.
|
PROFIT
My goals were predominantly financial. I realized that being money-driven was
difficult for me, but
in business success is usually equated with accumulation
of financial wealth.
Don't get greedy, however; don't try to do too much all at
once.
|
 |
TARGET
+ FLUENCY
Defining a product’s target market is very difficult.
You also cannot assume that a product will move fluently from
one market to another. Know your target but also be willing to
change if it seems necessary. Although I was sure of my general target market, I
didn’t consider the “pop culture” of the 18 – 24
post-secondary markets. I should have also paid closer attention to the geographical
influence on each specific target market. These things require a lot of research prior to a product
launch.
|
EGGS
Don't put all your eggs in one basket;
try not to become
obsessed with only your new product.
While inventing the Study Buddy I became obsessed. My entire life was dedicated to inventing, gaining the
financing required, researching and launching the product. I took an entire summer between
second and third
year of university to bring this product to the market. This put an enormous amount of stress on me. I had not considered what would happen if it didn’t
work. My suggestion
to any budding entrepreneur is that they start a business while
working full-time and once the business becomes successful
enough they leave their full-time position to run the business.
|
 |
DEADLINES
I took an absolutist approach to deadlines. Instead of realizing that the deadlines
I had set
for myself were unrealistic, I produced a mediocre piece of
work. Entrepreneurs
must take a flexible approach to deadlines. My problem was that I was running out of funds and that
is another reason I rushed.
SHORTAGE
You can have a shortage of product if
it sells too quickly, and you also can have a shortage of sales
when the hoped-for response doesn’t materialize.
A marketer should be cognizant of the possibility of
failure. However, there is also the argument that if one is attempting
to achieve something, they should put everything they have in to
it. Entrepreneurial
Quote “You will never know how close you were to success if
you give up”
|
RELIANCE
Don't rely on just one product and
don't forget your "old" products. Marketers should realize that there are many products on
the market that can fulfill the same need as your product. Just because a product is new doesn’t mean it is
better. Have something to
fall back on.
|
 |
|
The New-Product
Development Process
 |
Exercise
- Plan
New Product
Development |
Which of
these things was most important in your launching of a new
product, and why?
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
The Product Life Cycle
Stages in the Product Life
Cycle
|
Check out how advertising is used in different stages of the Product
Life Cycle, in the Unit on
Promotion |
Styles, Fashions and Fads
|
Style |
Basic and distinctive mode of
expression |

Formal Clothing |
|
Fashion |
Popular style in a particular
field |

Business Casual |
|
Fad |
Fashion that
enters quickly
is adopted quickly
declines quickly |

Pet Rocks |
 |
Exercise - Plan
Your Plan Product - Style, Fasion, or Fad? |
Which of these three most closely describes your Marketing
Plan product? (Don't say "none" - pick the one that is
closest and explain the fit).
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
III. Product and Service Decisions
Individual
Product Decisions
Product Attributes
Branding - So
important it has its own chapter
Packaging and Labelling
Packaging is so important to the
Marketing process that it is often called the Fifth P
There are main purposes to Packaging
| Protection |
 |
Example:
Protect breakable products, or keep many
small parts safely together |
| Promotion |
  |
Example:
Cosmetics and perfumes cost very little to
make but pretty packaging allows a huge markup and profit |
| Information |
 |
Example:
Changing the consumer's perception of your
product with anew and different package |
|
Convenience |
 |
Example:
Hold ready-made dinners |
| Unitization |
 |
Example:
Group products according to consumer, retail, and
transportation |
| Handling |
 |
Example:
Shipping product to retailers |
 |
Exercise:
Lab
Packaging |
Go
to a store where you shop frequently and find one
specific example each of each of the three
purposes of packaging. Tell us about them.
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
Labelling
Product Support
Services
 |
Exercise
- Plan
Competitive Advantage |
What are you offering your customers
in your Marketing Plan in the way of product support services that gives you a competitive advantage?
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
Product Line Decisions
| Product Line Length |
add or subtract items in the present
range |
|
| Up-Selling |
Move customers up to higher models
BMW wants customers to move from
the 3-series models to the 5 and 7 series |
 |
| Cross-Selling |
Hewlett Packard
sells printers as well as cartridges |
 |
|
Down-Selling |
add lower quality products that
sell for less
Daimler-Chrysler
stretched Mercedes down with a cheaper version in a slow marker |
 |
|
Filling Within Current Range |
Fill in both directions
Mariott Hotels
added Renaissance (up) and TownePlace Suites (down) |
 |
Product Mix
Decisions
 |
Exercise
Product Mix |
What is
Marriott Hotels trying to do with this product mix strategy?
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
 |
Exercise

Extensions |
How might your Marketing Plan use the Product Line
Stretch in the future?
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
IV. Services Marketing
Good Service is
important in Marketing. Take this company's brag on its
truck:

In case you can't read it, it says, "Quality
Service since 3:00 last Thursday!
(picture provided by Milt Chamberlain) |
 |
Nature and Characteristics of a
Service
Marketing Strategies for Service
Firms
Three Types of Service Marketing
| Internal Marketing |
Train and Motivate Customer-Contact Employees |
| External Marketing |
All the rest of Marketing |
| Interactive Marketing |
Quality of the Buyer-Seller Interaction |
Additional
Product Considerations
Product Decisions and
Social Responsibility
 |
Exercise
Social Responsibility |
Describe one area in which your product might be either
socially responsible or potentially harmful to someone.
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
International
Product and Services Marketing
Chapter 9: Branding
Strategy and Management
I. What is a Brand?
Brand Meaning
Brand
Relationships
People as Brands
II. Brand
Characteristics
Logos -
It's sometimes necessary to update a
brand, but it's often difficult to do so because customers object
Brand
Personality - Brands have
different personalities just as people do; it's part of why it can
be so difficult to change a brand
Brand Equity:
adds value
assures quality
gets preference
ensures original
protects features
increases markets
builds image
|
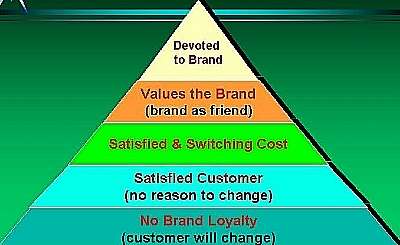 |
 |
Exercise
Brand Equity |
Choose a
product you buy either regularly or occasionally and tell
us which layer of the pyramid your product purchase fits
into
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
III. Branding
Strategy and Management
| Brand Name Selection |
Pick a
name that
suggests something about the product
is easy to pronounce
is distinctive
is extendable
can translate easily
is capable of registration and legal protection
 |
Exercise
- Plan
Brand Name |
For
your Marketing Plan product, which of these requirements
does your brand name meet? What might you have to change
about your chosen brand name in order to meet these requirements?
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
|
| Brand
Positioning |
| Position Dove Soap on: |
 |
| Product Attributes |
1/4 moisturizing lotion |
| Desirable Benefits |
Softer Skin |
| Beliefs and Values |
"A healthier more democratic view of
beauty" |
|
| Brand Sponsorship |
National and Private Brands
Licensing
Co-branding |
| Brand
Development |
Line extensions
Multi-brands
New brands
- choose new strategy for new brand
Individual Brand Names
P&G
makes 8 different brands of detergent |

|
Blanket Family Name
Everything
Coca-Cola makes carries its name |
 |
Separate Family Name
At Sears, think:
Kenmore Washers
Craftsman Tools |
 |
Company Trade Name/
Individual Product Name
Quaker Oats
Cap'n Crunch appeals to both parent & child |
 |
|
| Ongoing
Brand Management |
To keep a brand, you need
to police its use
Continual Communication to Customer
Brand Experience through advertising, work of mouth, personal
interaction
Employees as customer-centred brand builders
Brand equity managers
Brand Audits
Rebranding when necessary |
IV. Brand
Communications
Brand Experiences and Touchpoints
 |
Exercise
Touchpoints |
Tell us
one of your favourite brands and describe a "touchpoint"
you experience with that brand.
Post your answer in the
Moodle Discussion Group. |
|
Brand Icons and Characters
- Read carefully the text's description
of the M&M characters to understand what we mean when we say a
brand has "personality".
Brand Ambassadors
- Check out Benetton's ad to see some
of the people described in the text
Brand Stories -
Branded Content and Entertainment
Brands and Social Media -
Brand Advocates
|